PAGE AUTHOR
MATT JONES, MD
CONSULTING SPECIALIST
DON BYARS, MD
IMAGE CONTRIBUTOR
MATT JONES, MD
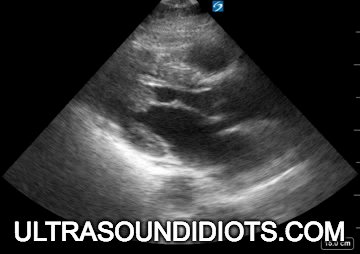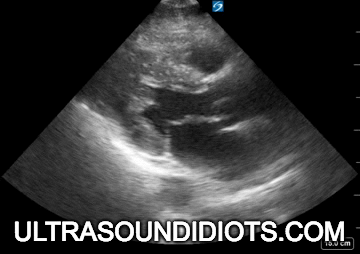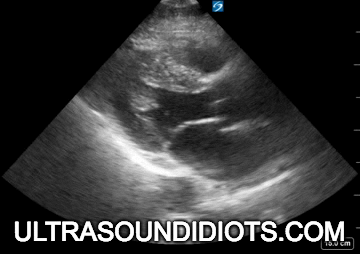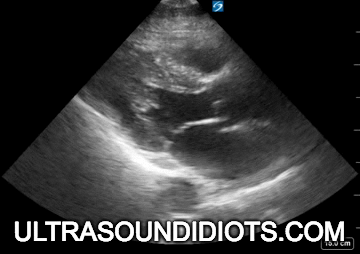
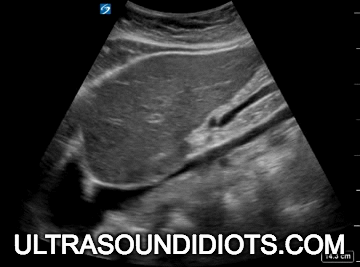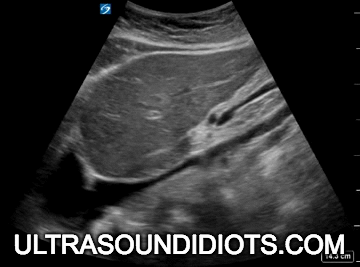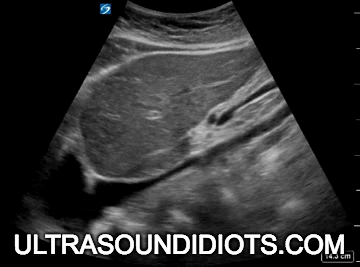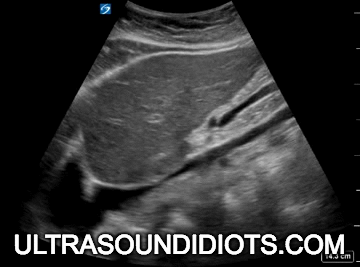
Diagnostic TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
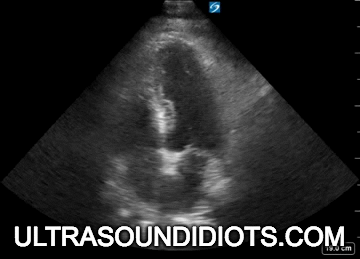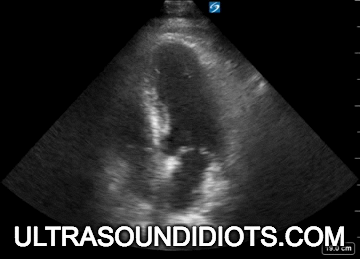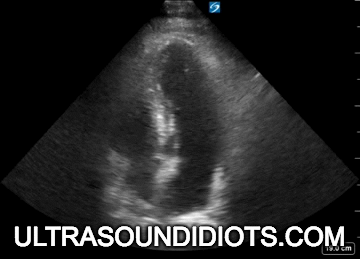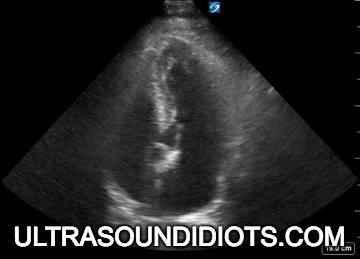
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function
gross assessment
left ventricular squeeze - approx 50%
EPSS - should be < 5mm
MAPSE - don't measure, look for good movement
If you want to measure
Fractional Shortening
Teichholz
Modified Simpson (most accuarte)
End Point Septal Separation (EPSS)
IVC
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function
Think of diastolic function as how well the ventricles relax. Diastolic dysfunction (or stiffness) is most often a result of ventricular hypertrophy secondary to hypertension. Other causes include...
Diastolic Function Lecture
http://www.criticalecho.com/sites/default/files/images/6.13.png
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qdLkbcFe_DI
Supernormal Diastolic function
need example
Normal Diastolic Function
Diastolic dysfunction, Grade 1
(Abnormal relaxation)
diastolic dysfunction, grade 2 (pseudonormal)
diastolic dysfunction, grade 3 (restrictive)
Evaluation of Right Ventricle
Gross Assessment of RV function
Observe for normal ventricular contraction. You want to see no free wall hypokinesis.
RV dilation/enlargement, normal RV/LV basal diameter ratio 1/3 to 1/2
Evidence of RV overload
Apical Blunting
Deviation of interventricular septum toward LV
Dilated IVC
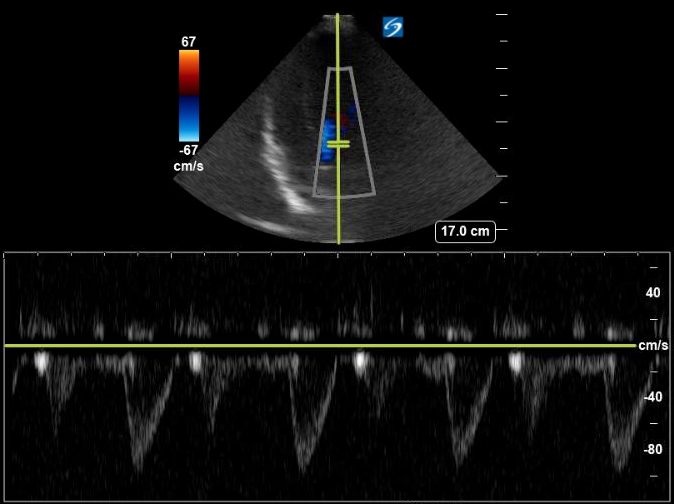
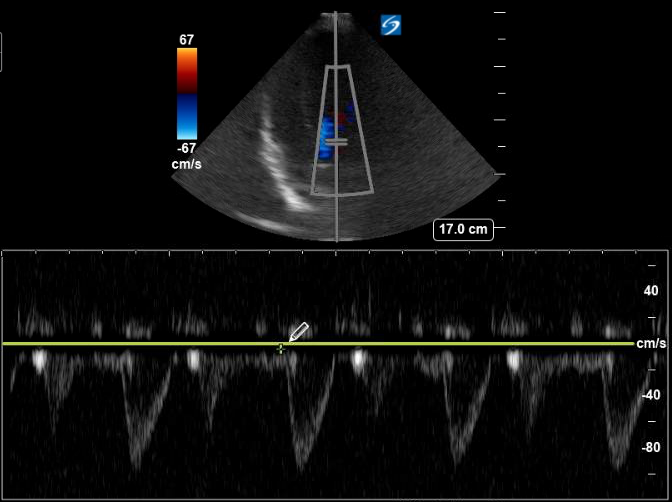
Doppler
Color Doppler
Observe for tricuspid regurgitation
Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion (TAPSE) with M-mode
TAPSE <1.6 cm is abnormal
Right Ventricular Systolic Pressure (RVSP)
RVSP = 4[(TRmax)^2] + RAP
Normal RSVP is 35mmhg
TRmax is the max velocity of tricuspid regurgitation in m/s
RAP is Right Atrial Pressure
To calculate Right Atrial Pressure
VTI
(Velocity Time integral)