Authors
Matt Jones, MD, MS, RDMS, RDCS
Tae Kim, MD, RDMS
COntributors
matt jones, MD
GIORGI TSEREDIANI, MD
Shravan Kumar, MD
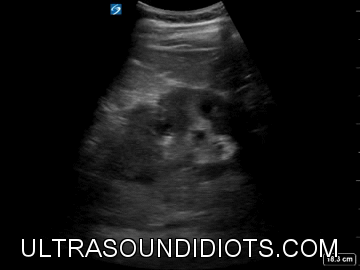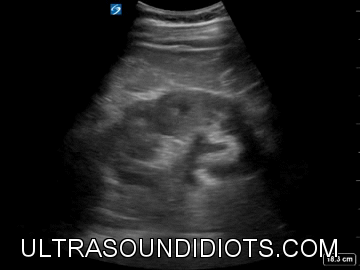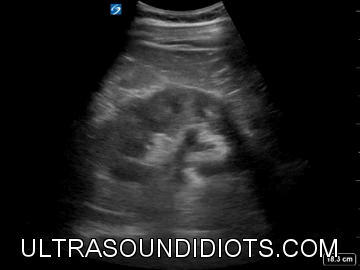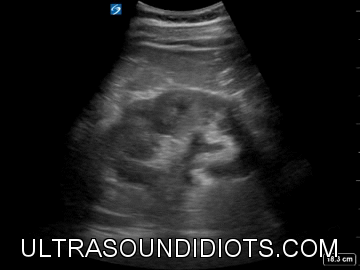
Renal / Bladder
RIGHT KIDNEY
LONG AXIS (LONGITUDINAL) VIEW
Probe in the right lower intercostal space (8th to 11th) in the mid-axillary line
Probe marker toward patient’s head and aim the probe slightly posteriorly
Locate liver-kidney interface
Right kidney is often found more anteriorly than left kidney
Rock probe anteriorly and posteriorly to scan the entire kidney in longitudinal section
*** The liver is a very large acoustic window... The probe can come anterior as far as anterior axillary line with adequate renal views.
ANIMATION
SHORT AXIS (TRANSVERSE) VIEW
Probe in the right lower intercostal space (8th to 11th) in the mid-axillary line
Rotate the probe 90°, probe marker points toward the ceiling
Rock the probe superiorly and posteriorly to scan the entire kidney in transverse section
ANIMATION
LEFT KIDNEY
LONG AXIS (LONGITUDINAL) VIEW
Probe in the left lower intercostal space (6th -9th rib) at the posterior-axillary line. Probe contact needs to be posterior (retroperitoneal organ).
Probe marker toward patient’s head and aim the probe slightly posteriorly
Locate spleen-kidney interface
Left kidney is often found more superiorly and posteriorly than right kidney
Rock probe anteriorly and posteriorly to scan the entire kidney in longitudinal section
ANIMATION
SHORT AXIS (TRANSVERSE) VIEW
Probe in the left lower intercostal space (6th to 9th) in the mid-axillary line
Rotate the probe 90°, probe marker points toward the floor
Rock the probe superiorly and posteriorly to scan the entire kidney in transverse section
ANIMATION
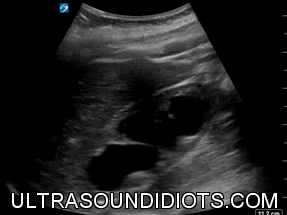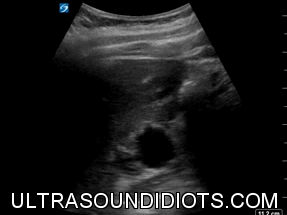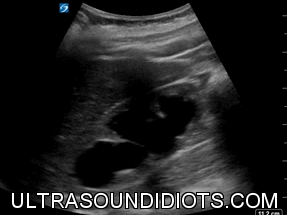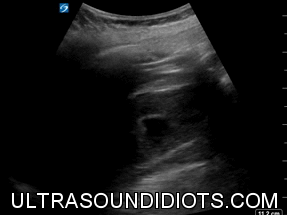
HYDRONEPHROSIS
NORMAL KIDNEY
ANIMATION
MILD HYDRONEPHROSIS
ANIMATION
MODERATE HYDRONEPHROSIS
ANIMATION
SEVERE HYDRONEPHROSIS
ANIMATION
BLADDER
LONGITUDINAL VIEW
Probe placed midline just superior to the pubic bone
Probe marker toward patient’s head
Apply downward pressure and slide up probe slightly superiorly
Fan the probe left and right to scan the entire bladder in sagittal section
ANIMATION
TRANSVERSE VIEW
Probe placed midline just superior to the pubic bone
Rotate the probe 90°, probe marker toward patient’s right
Rock the probe superiorly and inferiorly to scan the entire bladder in transverse section
ANIMATION
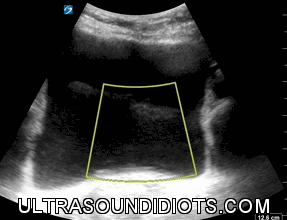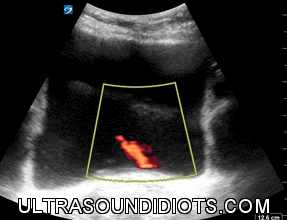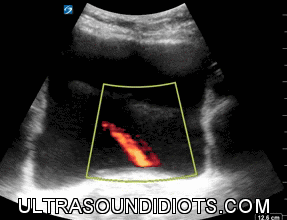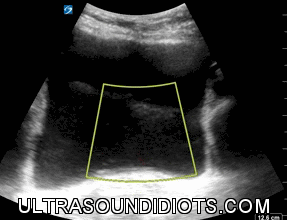
Ureteral Jets
CALCULATING BLADDER VOLUME
BLADDER VOLUME = LENGTH (SAGITTAL) × HEIGHT (TRANSVERSE) × WIDTH (TRANSVERSE) × 0.625
SAGITTAL MEASUREMENT
Calculate maximum length
ANIMATION
TRANSVERSE MEASUREMENT
Calculate maximum height and width
ANIMATION
BMI 57
Foley in place with inflated balloon. Bladder is decompressed.